集合框架
集合只能存储引用数据类型(对象)。当存储基本数据类型的时候会自动装箱
集合体系:
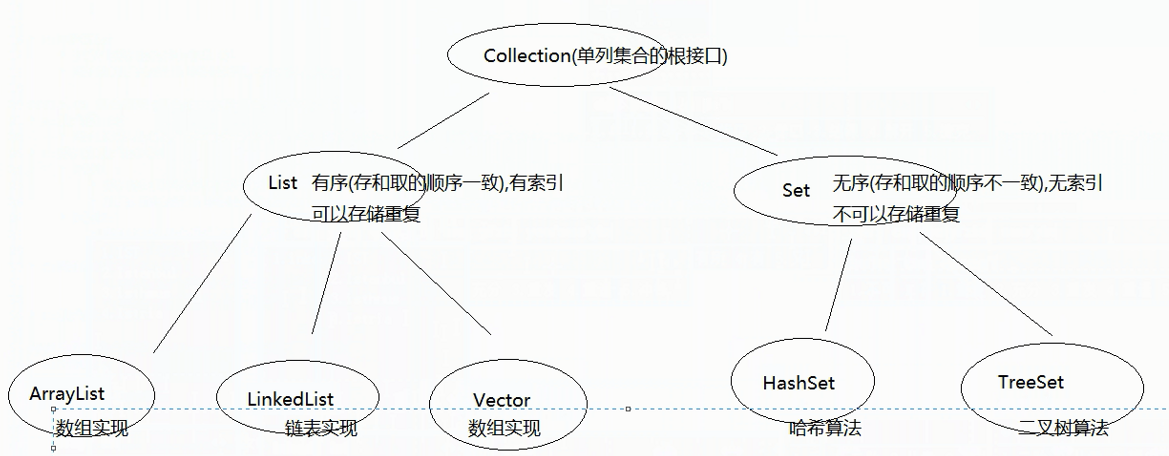
Collection接口
- boolean add(E e)
- boolean remove(Object o)
- void clear()
- boolean contains(Object o)
- boolean isEmpty()
- int size()
- toArray() : 把集合转成数组
- boolean addAll(Collection c)
- boolean removeAll(Collection c) : 删除的是交集
- boolean containsAll(Collection c)
- boolean retainAll(Collection c) : 取交集,如果调用的集合发生改变就返回true,如果调用的集合不变就返回false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
public class Testing5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
boolean b1 = c.add("abc");
boolean b2 = c.add(true);
boolean b3 = c.add(100);
boolean b4 = c.add("abc");
boolean b5 = c.remove(b3);
System.out.println(b1);
System.out.println(c.toString());
Object[] arr = c.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
|
List的接口
- void add(int index,E element)
- E remove(int index)
- E get(int index)
- E set(int index,E element)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Testing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add(4, "f");
System.out.println(list);
Object a = list.remove(2);
System.out.println(a);
Object b = list.get(3);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(list);
Object c = list.set(0, "hyl");
System.out.println(c);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
List的并发修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
li = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
for each in li:
if each == 5:
li.append("hyl")
print(li)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Testing5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("world");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String str = (String)it.next();
if("world".equals(str)) {
list.add("javaee");
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
并发修改,遍历的同时在增加元素,引发concurrentModificationException
需要改为listIterator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class Testing3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a")
list.add("b");
list.add("world");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
ListIterator lit = list.listIterator();
while(lit.hasNext()) {
String str = (String)lit.next();
if("world".equals(str)) {
lit.add("javaee");
}
}
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
去除List中的重复引用类型(对象)
- contains方法判断是否包含,底层依赖的是equals方法
- remove方法判断是否删除,底层依赖的是equals方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
Person p = (Person)obj;
return this.name.equals(p.name) && this.age == p.age;
}
}
public class Testing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Person("张三", 23));
list.add(new Person("张三", 23));
list.add(new Person("李四", 24));
list.add(new Person("李四", 24));
ArrayList newList = getSingle(list);
System.out.println(newList);
list.remove(new Person("张三", 23));
System.out.println(list);
}
public static ArrayList getSingle(ArrayList list) {
ArrayList newList = new ArrayList<>();
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Object obj = it.next();
if(!newList.contains(obj)) {
newList.add(obj);
}
}
return newList;
}
}
|
ArrayList嵌套ArrayList
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| public class Demo5_ArrayListArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Person>> list = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Person> first = new ArrayList<>();
first.add(new Person("杨幂", 30));
first.add(new Person("李冰冰", 33));
first.add(new Person("范冰冰", 20));
ArrayList<Person> second = new ArrayList<>();
second.add(new Person("黄晓明", 31));
second.add(new Person("赵薇", 33));
second.add(new Person("陈坤", 32));
list.add(first);
list.add(second);
for(ArrayList<Person> a : list) {
for(Person p : a) {
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}
}
|
Vector的接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Demo5_Vector {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector v = new Vector();
v.addElement("a");
v.addElement("b");
v.addElement("c");
v.addElement("d");
Enumeration en = v.elements();
while(en.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println(en.nextElement());
}
}
}
|
LinkedList的接口
-
public void addFirst(E e) 及 addLast(E e)
-
public E getFirst() 及 getLast()
-
public E removeFirst() 及 public E removeLast()
-
public E get(int index);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class Demo3_LinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.addFirst("a");
list.addFirst("b");
list.addFirst("c");
list.addFirst("d");
list.addLast("e");
System.out.println(list.getFirst());
System.out.println(list.getLast());
System.out.println(list.removeFirst());
System.out.println(list.removeLast());
System.out.println(list.get(1));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
HashSet的接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import java.util.HashSet;
public class Demo1_HashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<>();
boolean b1 = hs.add("a");
boolean b2 = hs.add("a");
hs.add("b");
hs.add("c");
hs.add("d");
System.out.println(hs);
System.out.println(b1);
System.out.println(b2);
for (String string : hs) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}
|
HashSet原理
- 我们使用Set集合都是需要去掉重复元素的, 如果在存储的时候逐个equals()比较, 效率较低,哈希算法提高了去重复的效率, 降低了使用equals()方法的次数
- 当HashSet调用add()方法存储对象的时候, 先调用对象的hashCode()方法得到一个哈希值, 然后在集合中查找是否有哈希值相同的对象
- 如果没有哈希值相同的对象就直接存入集合
- 如果有哈希值相同的对象, 就和哈希值相同的对象逐个进行equals()比较,比较结果为false就存入, true则不存
- 将自定义类的对象存入HashSet去重复
- 类中必须重写hashCode()和equals()方法
- hashCode(): 属性相同的对象返回值必须相同, 属性不同的返回值尽量不同(提高效率)
- equals(): 属性相同返回true, 属性不同返回false,返回false的时候存储
LinkedHashSet的接口
HashSet的子类。底层是链表实现的。
LinkedHashSet的特点 : 可以保证怎么存就怎么取(有点类似于python中的orderdict)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class Testing4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<String> lhs = new LinkedHashSet<>();
lhs.add("a");
lhs.add("b");
lhs.add("b");
lhs.add("c");
lhs.add("d");
System.out.println(lhs);
}
}
|
TreeSet的接口
TreeSet集合是用来对象元素进行排序的。他也可以保证元素的唯一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Testing5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<>();
ts.add(1);
ts.add(5);
ts.add(7);
ts.add(6);
ts.add(3);
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
|
如果元素是自定义对象 ,
方法一 : 实现Comparable接口,并且重写compareTo方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Testing5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Person> ts = new TreeSet<>();
ts.add(new Person("hyl",21));
ts.add(new Person("czj",22));
ts.add(new Person("gzr",21));
ts.add(new Person("dsz",23));
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
public String name;
public int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[Person:" + name + " " + age + "]" ;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
|
方法二 : 编写类A,类A实现Comparator接口 . TreeSet的构造器传入给类实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Testing2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<>(new CompareByLen());
ts.add("aaaaaaa");
ts.add("cc");
ts.add("bAA");
ts.add("WC");
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
class CompareByLen implements Comparator<String> {
@Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
int num = s1.length() - s2.length();
return num == 0 ? s1.compareTo(s2) : num;
}
}
|
总结两种方法:
- 自然顺序(Comparable)
- TreeSet类的add()方法中会把存入的对象提升为Comparable类型
- 调用对象的compareTo()方法和集合中的对象比较
- 根据compareTo()方法返回的结果进行存储
- 比较器顺序(Comparator)
- 创建TreeSet的时候可以制定 一个Comparator
- 如果传入了Comparator的子类对象, 那么TreeSet就会按照比较器中的顺序排序
- add()方法内部会自动调用Comparator接口中compare()方法排序
- 调用的对象是compare方法的第一个参数,集合中的对象是compare方法的第二个参数
两种方式的区别
- TreeSet构造函数什么都不传, 默认按照类中Comparable的顺序(没有就报错ClassCastException)
- TreeSet如果传入Comparator, 就优先按照Comparator
练习 : 在一个集合中存储了无序并且重复的字符串,定义一个方法,让其有序(字典顺序),而且还不能去除重复 (实际上就是使用搜索二叉树的性质进行排序)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
list.add("ccc");
list.add("ddd");
list.add("fffffffffff");
list.add("heima");
list.add("itcast");
list.add("bbbb");
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
public static void sort(List<String> list) {
TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
int num = s1.compareTo(s2);
return num == 0 ? 1 : num;
}
});
ts.addAll(list);
list.clear();
list.addAll(ts);
}
}
|
List和Set总结
- List
- 普通for循环, 使用get()逐个获取
- 调用iterator()方法得到Iterator, 使用hasNext()和next()方法
- 增强for循环, 只要可以使用Iterator的类都可以用
- Vector集合可以使用Enumeration的hasMoreElements()和nextElement()方法
- Set
- 调用iterator()方法得到Iterator, 使用hasNext()和next()方法
- 增强for循环, 只要可以使用Iterator的类都可以用
数组转为集合
使用Arrays.asList
数组转换成集合Collection , 虽然不能增加或减少元素,但是可以用集合的思想操作数组,也就是说可以使用其他集合中的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class Demo4_AsList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arr = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(arr);
System.out.println(list);
}
}
|
将数组转换成集合,数组必须是引用数据类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Testing2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {11,22,33,44,55};
List<int[]> list = Arrays.asList(arr);
System.out.println(list);
Integer[] arr2 = {11,22,33,44,55};
List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(arr2);
System.out.println(list2);
}
}
|
集合转为数组
使用toArray
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Testing3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
String[] arr = list.toArray(new String[10]);
for (String string : arr) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}
|
Collections工具类
- Collections类概述 : 针对集合操作 的工具类
- 成员方法 : 全部都是静态方法
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list)public static <T> int binarySearch(List<?> list,T key)public static <T> T max(Collection<?> coll)public static void reverse(List<?> list)public static void shuffle(List<?> list)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Testing2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
arr.add(33);
arr.add(55);
arr.add(22);
arr.add(11);
arr.add(44);
Collections.sort(arr);
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
|
Map的接口
Map接口和Collection接口的不同
- Map是双列的,Collection是单列的
- Map的键唯一,Collection的子体系Set是唯一的
- Map集合的数据结构值针对键有效,跟值无关;Collection集合的数据结构是针对元素有效
方法:
V put(K key,V value):添加元素。void clear():移除所有的键值对元素V remove(Object key):根据键删除键值对元素,并把值返回boolean containsKey(Object key):判断集合是否包含指定的键boolean containsValue(Object value):判断集合是否包含指定的值boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet(): 返回此映射中包含的映射关系的Set视图。V get(Object key):根据键获取值Set<K> keySet():获取集合中所有键的集合Collection<V> values():获取集合中所有值的集合int size():返回集合中的键值对的个数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import java.util.HashMap;
public class Testing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Integer i1 = map.put("hyl", 21);
Integer i2 = map.put("czj", 20);
Integer i3 = map.put("dsz", 23);
Integer i4 = map.put("grz", 24);
Integer i5 = map.put("grz", 25);
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(i2);
System.out.println(i3);
System.out.println(i4);
System.out.println(i5);
}
}
|
遍历Map
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Testing2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Integer i1 = map.put("hyl", 21);
Integer i2 = map.put("czj", 20);
Integer i3 = map.put("dsz", 23);
Integer i4 = map.put("grz", 24);
Set<String> ks = map.keySet();
Iterator<String> it = ks.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String key = it.next();
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
}
}
|
或者
1
2
3
| for(String key:map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + "=" + map.get(key));
}
|
或者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("张三", 23);
map.put("李四", 24);
map.put("王五", 25);
map.put("赵六", 26);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it = entrySet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Integer> en = it.next();
String key = en.getKey();
Integer value = en.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}
|
或者
1
2
3
| for(Entry<String, Integer> en : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(en.getKey() + "=" + en.getValue());
}
|
HashMap嵌套HashMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| public class Demo8_HashMapHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Student, String> hm88 = new HashMap<>();
hm88.put(new Student("张三", 23), "北京");
hm88.put(new Student("李四", 24), "北京");
hm88.put(new Student("王五", 25), "上海");
hm88.put(new Student("赵六", 26), "广州");
HashMap<Student, String> hm99 = new HashMap<>();
hm99.put(new Student("唐僧", 1023), "北京");
hm99.put(new Student("孙悟空",1024), "北京");
hm99.put(new Student("猪八戒",1025), "上海");
hm99.put(new Student("沙和尚",1026), "广州");
HashMap<HashMap<Student, String>, String> hm = new HashMap<>();
hm.put(hm88, "第88期基础班");
hm.put(hm99, "第99期基础班");
for(HashMap<Student, String> h : hm.keySet()) {
String value = hm.get(h);
for(Student key : h.keySet()) {
String value2 = h.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value2 + "=" + value);
}
}
}
}
|
LinkedHashMap的接口
底层是链表实现的可以保证怎么存就怎么取
类似于python中的orderdict
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class Testing3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<String,Integer> lhm = new LinkedHashMap<>();
lhm.put("hyl", 21);
lhm.put("czj", 22);
lhm.put("gzr", 23);
lhm.put("hyl", 24);
System.out.println(lhm);
}
}
|
TreeMap的接口
自动排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class Testing4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer,String> tm = new TreeMap<>();
tm.put(2,"hyl");
tm.put(1,"czj");
tm.put(4,"gzr");
tm.put(3,"dsz");
System.out.println(tm);
}
}
|
就像是TreeSet , 如果要比较自定义引用类型的话 . 二选一
- 实现Comparable接口,并且重写compareTo方法
- 编写类A,类A实现Comparator接口 . TreeSet的构造器传入给类实例
HashMap和Hashtable的区别
- Hashtable是线程安全的,效率低,
HashMap是线程不安全的,效率高
- Hashtable不可以存储null键和null值,
HashMap可以存储null键和null值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class Testing5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Integer> hm = new HashMap<>();
hm.put(null,1);
hm.put("h",null);
System.out.println(hm);
}
}
|
Collection和Map总结
迭代器
iterator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Testing5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("abc");
c.add(true);
c.add(100);
Iterator iter = c.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iter.next());
}
}
}
|
ListIterator
能有后往前迭代
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class student2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("world");
list.add("c");
list.add("d");
list.add("e");
ListIterator lit = list.listIterator();
while(lit.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(lit.next());
}
System.out.println("-----------------");
while(lit.hasPrevious()) {
System.out.println(lit.previous());
}
}
}
|
泛型概述和基本使用
- 容器只能存储某个类型的数据
- 泛型好处
- 提高安全性(将运行期的错误转换到编译期)
- 省去强转的麻烦
- 泛型基本使用 :
<>中放的必须是引用数据类型
- 泛型使用注意事项 : 前后的泛型必须一致,或者后面的泛型可以省略不写
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Demo1_Generic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Person> list = new ArrayList<Person>();
list.add(new Person("张三", 23));
list.add(new Person("李四", 24));
Iterator<Person> it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Person p = it.next();
System.out.println(p.getName() + "..." + p.getAge());
}
}
|
使用Object模仿泛型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public class Student extends Person {
public Student() {}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
}
public class Worker extends Person {
public Worker() {}
public Worker(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
}
public class Tool {
private Object obj;
public Object getObj() {
return obj;
}
public void setObj(Object obj) {
this.obj = obj;
}
}
public class Demo3_Generic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool t = new Tool();
t.setObj(new Student("张三",23));
Worker w = (Worker) t.getObj();
System.out.println(w);
}
}
|
泛型方法
把泛型定义在方法上
简单来说 , 一个容器类可能有方法
这个容器已经有泛型 , 也就是说在实例化这个容器类的时候就规定了元素的类型B
工具类的方法的参数的数据类型一般都是B . 但是如果想传入其他类型的数据,那么就要设置该方法的泛型
- 因为静态方法是由类直接调用的,而我们确定泛型的值是在实例化的时候
- 所以静态方法必须要有自己的泛型
定义格式 : public <泛型类型> 返回类型 方法名(泛型类型 变量名)
静态方法必须有自己的泛型
示例 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class Tool<Q> {
private Q q;
public Q getObj() {
return q;
}
public void setObj(Q q) {
this.q = q;
}
public<T> void show(T t) {
System.out.println(t);
}
public static<W> void print(W w) {
System.out.println(w);
}
}
public class Demo3_Generic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tool<String> t = new Tool<>();
t.show(true);
}
}
|
泛型接口
泛型接口概述 : 把泛型定义在接口上。定义格式 : public interface 接口名<泛型类型>
示例 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| interface Inter<T> {
public void show(T t);
}
class Demo implements Inter<String> {
@Override
public void show(String t) {
System.out.println(t);
}
}
|
泛型通配符
泛型通配符 :
<?> : 任意类型,如果没有明确,那么就是Object以及任意的Java类了? extends E : 泛型固定上边界,向下限定,E及其子类? super E : 泛型固定下边界,向上限定,E及其父类
1
2
|
List<?> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class Demo5_Generic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Person> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(new Person("张三", 23));
list1.add(new Person("李四", 24));
list1.add(new Person("王五", 25));
ArrayList<Student> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add(new Student("赵六", 26));
list2.add(new Student("周七", 27));
list1.addAll(list2);
System.out.println(list1);
}
}
|
这里的addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)表示这里的addAll方法能接受E类, 也能接受E的子类
三种迭代的能否删除
- 普通for循环,可以删除,但是索引要
i--
- 迭代器,可以删除,但是必须使用迭代器自身的remove方法,否则会出现并发修改异常
- 增强for循环不能删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class Testing2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
arr.add(1);
arr.add(1);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(3);
arr.add(4);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if(arr.get(i)==2){
arr.remove(i--);
}
}
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class Testing2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
arr.add(1);
arr.add(1);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(3);
arr.add(4);
Iterator<Integer> it = arr.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
if (it.next()==2) {
it.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
|
静态导入
格式:
import static 包名….类名.方法名;- 可以直接导入到方法的级别
注意事项
- 方法必须是静态的,如果有多个同名的静态方法,容易不知道使用谁?这个时候要使用,必须加前缀。
- 由此可见,意义不大,所以一般不用,但是要能看懂。
原先 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import java.util.Arrays;
public class Testing3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {9,6,5,8,7,4,1,2,3};
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}
|
现在 :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import static java.util.Arrays.sort;
public class Testing4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {9,6,5,8,7,4,1,2,3};
sort(arr);
}
}
|
可变参数
可变参数概述 : 定义方法的时候不知道该定义多少个参数
格式 : 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(数据类型… 变量名){}
注意事项:
- 可变参数其实就是一个数组
- 如果一个方法有可变参数,并且有多个参数,那么,可变参数肯定是最后一个
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class Testing4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {9,6,5,8,7,4,1,2,3};
printArr(arr);
printArr(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8);
}
public static void printArr(int...arr) {
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
|
和python一样 , 同样有截取参数的情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Testing5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
printArr(1,2,3);
}
public static void printArr(int hyl,int...arr) {
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
|
