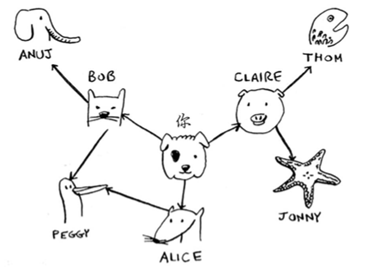
使用散列表实现图 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 neighbor = {} neighbor['you' ] = ['alice' ,'bob' ,'claire' ] neighbor['bob' ] = ['anuj' ,'peggy' ] neighbor['alice' ] = ['peggy' ] neighbor['claire' ] = ['thom' ,'jonny' ] neighbor['anuj' ] = [] neighbor['peggy' ] = [] neighbor['thom' ] = [] neighbor['jonny' ] = []
广度优先的复杂度为O(边数+人数),简记为O(V+E)
任务A依赖于任务B,任务A就必须在任务B后面。这被称为拓扑排序
狄克斯特拉算法
适用 : 非负权重有向无环图
作用 : 起点到各个节点的最短距离
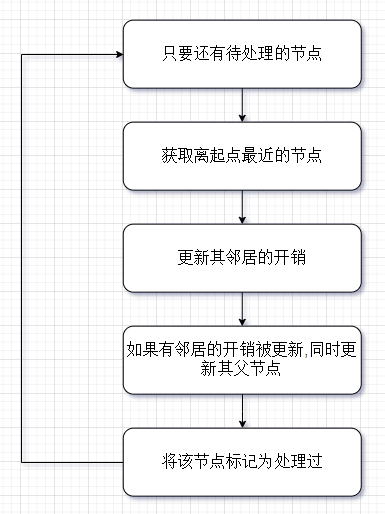
需要三个字典和一个数组:
一个嵌套字典用于模拟图。
一个字典用于存储起点到每个节点的开销。
一个字典用于存储每个节点的父节点。
一个数组用于存储处理过的节点。
处理逻辑:
得到:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 class Dijkstra : def __init__ (self,graph,start ): self.graph = graph self.costs = {} self.parents = {} self.processed = [] self.start = start def create_costs_dict (self ): for nodes,weight in self.graph[self.start].items(): self.costs[nodes] = weight def create_parents_dict (self ): for nodes in self.graph[self.start]: self.parents[nodes] = self.start def find_lowest_cost_node (self ): ''' 接受开销表为函数参数,返回开销最低的节点 ''' lowest_cost = float ('inf' ) lowest_cost_node = None for node in self.costs: val = self.costs.get(node) if val < lowest_cost and node not in self.processed: lowest_cost = val lowest_cost_node = node return lowest_cost_node def show_tot_route (self ): reverse_dict = dict (zip (self.parents.values(),self.parents.keys())) next_node = self.start res = self.start + ' ' while reverse_dict.get(next_node): next_node = reverse_dict.get(next_node) res += f'-> {next_node} ' return res def run (self ): self.create_costs_dict() self.create_parents_dict() while len (self.processed) != len (self.costs): lowest_cost_node = self.find_lowest_cost_node() next_nodes = graph[lowest_cost_node] for neighbor,weight in next_nodes.items(): new_costs = self.costs[lowest_cost_node] + weight if self.costs.get(neighbor): if self.costs[neighbor] > new_costs: self.costs[neighbor] = new_costs self.parents[neighbor] = lowest_cost_node else : self.costs[neighbor] = new_costs self.parents[neighbor] = lowest_cost_node self.processed.append(lowest_cost_node) route = self.show_tot_route() msg = '{:<13}: {}\n{:<13}: {}\n{:<13}: {}' .format ('CostsTable' ,self.costs, 'ParentsTable' ,self.parents, 'Route' ,route) return msg if __name__ == '__main__' : graph = {} graph['1' ] = {} graph['1' ]['2' ] = 1 graph['1' ]['3' ] = 12 graph['2' ] = {} graph['2' ]['4' ] = 3 graph['2' ]['3' ] = 9 graph['3' ] = {} graph['3' ]['5' ] = 5 graph['4' ] = {} graph['4' ]['3' ] = 4 graph['4' ]['5' ] = 13 graph['4' ]['6' ] = 15 graph['5' ] = {} graph['5' ]['6' ] = 4 graph['6' ] = {} dijkstra = Dijkstra(graph,'1' ) print (dijkstra.run())
动态规划:
将问题分成小问题,先解决小问题,再逐步解决大问题。
反向索引:
搜索引擎的工作原理:
现在假设有用户搜索hi,在这种情况下,搜索引擎需要检查哪些页面包含hi。搜索引擎发现页面A和B包含hi,因此将这些页面作为搜索结果呈现给用户。
列表计数比较法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 def check (str1,str2 ): list1 = [0 ]*26 list2 = [0 ]*26 for each_char in str1: pos = ord (each_char) - ord ('a' ) list1[pos] += 1 for each_char in str2: pos = ord (each_char) - ord ('a' ) list2[pos] += 1 for idx in range (len (list1)): if list1[idx] != list2[idx]: return False return True if __name__ == '__main__' : str1 = 'heart' str2 = 'earthw' print (check(str1,str2))
同理可以延伸出字典比较:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 def check (str1,str2 ): all_char_set = set (str1) | set (str2) all_char_dict1 = dict .fromkeys(all_char_set,0 ) all_char_dict2 = dict .fromkeys(all_char_set,0 ) for each_char in str1: all_char_dict1[each_char] += 1 for each_char in str2: all_char_dict2[each_char] += 1 return all_char_dict1 == all_char_dict2 if __name__ == '__main__' : str1 = 'heart' str2 = 'earth' print (check(str1,str2))
列表的contains操作符是O(n),字典的contains操作符是O(1)
凡是要==反转项的顺序==,都要想到栈
栈的方法
Stack()创建一个空的新栈。它不需要参数,并返回一个空栈。
push(item)将一个新项添加到栈的顶部。它需要item做参数并不返回任何内容。
pop()从栈中删除顶部项。它不需要参数并返回item。栈被修改。
peek()从栈返回顶部项,但不会删除它。不需要参数。不修改栈。
isEmpty()测试栈是否为空。不需要参数,并返回布尔值。
size()返回栈中的item数量。不需要参数,并返回一个整数。
二分法
左闭右开
mid = low + (high - low) // 2high = midreturn low
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution : def searchInsert (self, nums, target ) -> int : low = 0 high = len (nums) while low < high: mid = low + (high - low)//2 if nums[mid] > target: high = mid elif nums[mid] < target: low = mid + 1 else : return mid return low
map抽象数据类型
Map()创建一个新的map。它返回一个空的map集合。
put(key,val)向map中添加一个新的键值对。如果键已经在map中,那么用新值替换旧值。
get(key)给定一个键,获取存储在map中的值或None。
del()使用del map[key]形式的语句从map中删除键值对。
len()返回存储在map中的键值对的数量。
in()对于key in ma语句,如果给定的键在map中返回True,否则为False。